A simple guide to how the FEIE Standard Deduction applies for Americans overseas
All You Need to Learn About the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion and Its Link to the Basic Deduction
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) provides an important opportunity for united state citizens and resident aliens working abroad to decrease their taxed earnings. Comprehending the eligibility criteria and claiming procedure is important. The communication in between the FEIE and the common deduction can complicate tax technique. Bad moves in steering these rules can result in missed out on benefits. Exploring these aspects discloses important details for effective tax preparation and maximizing financial advantages.
Recognizing the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE)
The International Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) works as a crucial tax obligation arrangement for U.S. residents and resident aliens that work abroad, allowing them to leave out a significant section of their foreign-earned earnings from united state federal tax. This provision is essential for people living outside the USA, as it aids mitigate the economic worry of dual tax on earnings earned in foreign nations. By utilizing the FEIE, qualified taxpayers can lower their gross income substantially, promoting financial stability while living and working overseas. The exclusion amount is readjusted annually for inflation, guaranteeing it shows current financial problems. The FEIE is specifically beneficial for those in regions with a higher cost of living, as it allows them to retain more of their earnings. Understanding the mechanics and implications of the FEIE empowers expatriates to make educated economic decisions and optimize their tax obligation scenarios while residing abroad.
Eligibility Needs for the FEIE
To receive the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption, people have to satisfy certain qualification needs that consist of the Residency Test and the Physical Visibility Examination. In addition, employment standing plays an essential duty in identifying qualification for this tax advantage. Recognizing these standards is necessary for any person seeking to benefit from the FEIE.

Residency Examination Standard
Establishing qualification for the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) pivots on meeting particular residency examination standards. Mainly, people need to develop their tax obligation home in a foreign country and show residency through either the bona fide residence examination or the physical presence examination. The authentic home examination requires that a taxpayer has actually developed an irreversible house in an international nation for a continuous duration that spans a whole tax obligation year. This entails demonstrating intent to make the international place a primary home. Additionally, the taxpayer should display connections to the international country, such as safeguarding housing, employment, or household links. Satisfying these residency requirements is important for getting approved for the FEIE and efficiently lowering tax obligation obligations on earned revenue abroad.
Physical Presence Test
Fulfilling the residency criteria can also be achieved through the physical presence test, which supplies a different course for getting approved for the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) To satisfy this test, an individual should be physically existing in a foreign nation for a minimum of 330 complete days during a successive 12-month period. This need stresses the relevance of real physical presence, instead of simply maintaining a home abroad. The 330 days do not have to be consecutive, enabling flexibility in travel plans. This examination is particularly valuable for united state homeowners or citizens working overseas, as it allows them to leave out a substantial part of their international earned earnings from U. FEIE Standard Deduction.S. tax, therefore decreasing their general tax obligation liability
Work Status Needs
Eligibility for the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) hinges on details employment condition requirements that people need to satisfy. To qualify, taxpayers have to demonstrate that their earnings is stemmed from foreign sources, normally through employment or self-employment. They have to be either a united state citizen or a resident alien and maintain a tax home in a foreign nation. Additionally, individuals must satisfy either the Physical Presence Test or the Bona Fide Home Examination to develop their foreign status. Freelance people should report their internet incomes, guaranteeing they do not go beyond the recognized exclusion limitations. It's vital for applicants to preserve appropriate documents to corroborate their insurance claims relating to employment condition and foreign revenue throughout the tax year.
Exactly how to Declare the FEIE
Qualification Demands Discussed
For individuals looking for to profit from the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE), understanding the eligibility requirements is vital. To qualify, one have to meet two main examinations: the authentic house test or the physical presence test. The authentic home test relates to those that have actually developed a copyright in a foreign nation for a continuous period, generally a year or more. Alternatively, the physical visibility examination calls for individuals to be literally present in a foreign country for a minimum of 330 days throughout a 12-month period. FEIE Standard Deduction. Additionally, only earned revenue from international resources gets exclusion. Fulfilling these standards is important for taxpayers wanting to minimize their taxed income while staying abroad
Essential Tax Return
How can one properly assert the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE)? To do so, specific tax obligation kinds have to be used. The primary kind required is internal revenue service Kind 2555, which enables taxpayers to report international earned income and declare the exemption. This type requires comprehensive info about the person's international residency and the revenue earned while living abroad. Additionally, if asserting the exemption for real estate costs, Form 2555-EZ might be used for simpleness, given specific standards are satisfied. It is important to assure that all essential areas of the kinds are completed precisely to avoid hold-ups or concerns with the IRS. Understanding these types is essential for making best use of the benefits of the FEIE.
Filing Process Steps
Claiming the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) includes a collection of clear and orderly steps. People need to identify their eligibility, validating they satisfy the physical existence or bona fide house tests. Next off, they need to complete internal revenue service Kind 2555, detailing revenue gained abroad and any type of suitable exclusions. It is crucial to gather supporting documents, such as international income tax return and evidence of residence (FEIE Standard Deduction). After completing the kind, taxpayers ought to affix it to their annual tax obligation return, generally Form 1040. Filing electronically can improve this process, but guaranteeing exact information is essential. Individuals should keep duplicates of all submitted kinds and supporting files for future reference in case of audits or inquiries from the Internal revenue service.
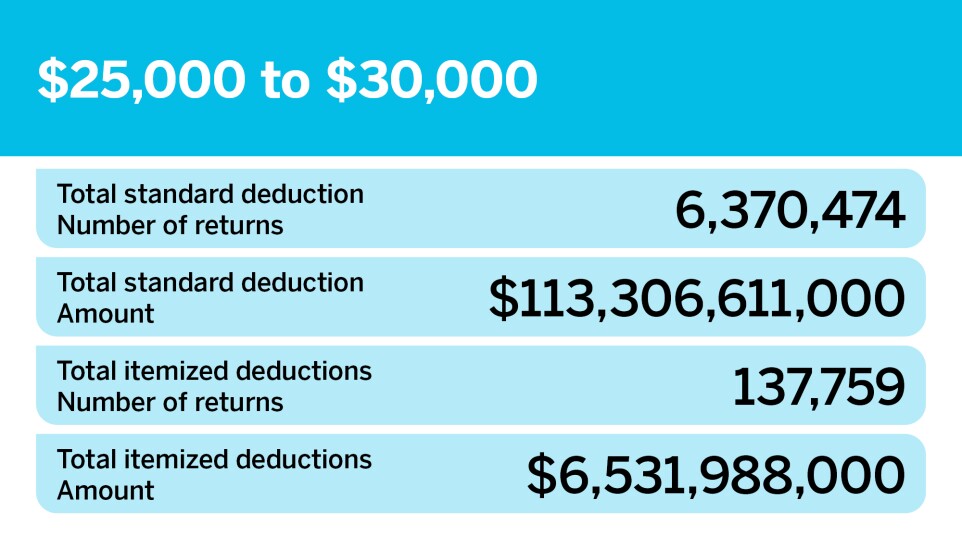
The Standard Reduction: A Summary
The typical deduction works as an essential tax advantage that streamlines the filing procedure for many people and households. This deduction enables taxpayers to reduce their taxed revenue without the need to itemize deductions, making it an appealing alternative for those with uncomplicated economic scenarios. For the tax year, the basic reduction amount varies based on filing condition, with different limits for single filers, wedded pairs submitting collectively, and heads of home.
The click here to read conventional reduction is changed every year for rising cost of living, guaranteeing its significance in time. Taxpayers who qualify can choose in between the typical deduction and itemizing their reductions, generally going with the higher advantage. By providing a sites baseline deduction, the common reduction supports taxpayers in lowering their overall tax obligation liability, consequently enhancing their financial position. Comprehending the common deduction is crucial for reliable tax preparation and making the most of possible financial savings for people and families alike.
Interaction In Between FEIE and Typical Deduction
While both the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) and the conventional reduction offer to lower taxed income, their interaction can substantially affect a taxpayer's total tax obligation. Taxpayers that get approved for the FEIE can exclude a substantial amount of their foreign-earned income, which may affect their eligibility for the conventional reduction. Specifically, if a taxpayer's foreign earnings is completely excluded under the FEIE, their gross income might drop listed below the threshold necessary to claim the typical reduction.
It is necessary to keep in mind that taxpayers can not double-dip; they can not use the exact same income to assert both the FEIE and the typical reduction. When determining the best technique for tax decrease, this indicates that mindful consideration is needed. Ultimately, understanding exactly how these two arrangements interact enables taxpayers to make enlightened choices, ensuring they maximize their tax obligation benefits while continuing to be certified with internal revenue service laws.
Tax Advantages of Using the FEIE
Using the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) can give noteworthy tax obligation advantages for U.S. residents and resident aliens living and working abroad. This exclusion enables eligible individuals to omit a particular quantity of foreign-earned revenue from their taxable earnings, which can lead to substantial tax savings. For the tax year 2023, the exclusion quantity is up to $120,000, markedly lowering the taxable revenue reported to the IRS.

Furthermore, the FEIE can assist stay clear of double taxes, as international taxes paid on this earnings may additionally be eligible for reductions or credit scores. By strategically making use of the FEIE, taxpayers can retain more of their earnings, enabling improved financial security. The FEIE can be helpful for those that qualify for the bona fide house test or physical existence examination, giving adaptability in managing their tax responsibilities while living overseas. In general, the FEIE is a useful device for migrants to maximize their monetary sources.

Usual Mistakes to Avoid With FEIE and Conventional Reduction
What pitfalls should taxpayers be mindful of when asserting the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) together with the conventional reduction? One typical error is thinking that both advantages can be claimed simultaneously. Taxpayers need to recognize that the FEIE needs to be asserted before the conventional reduction, as the exclusion fundamentally minimizes gross income. Stopping working to fulfill the residency or physical visibility tests can additionally bring about ineligibility for the FEIE, leading to unanticipated tax obligation liabilities.
Furthermore, some taxpayers overlook the need of appropriate paperwork, such as maintaining documents of international revenue and travel dates. One more frequent mistake is overestimating the exemption amount, possibly because of inaccurate forms or misinterpretation of tax obligation policies. Ultimately, people should remember that declaring the FEIE might affect qualification for certain tax debts, which can complicate their total tax scenario. Awareness of these challenges can help taxpayers navigate the complexities of global taxes better.
Often Asked Concerns
Can I Assert FEIE if I Live Abroad Part-Time?
Yes, a person can declare the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption if they live abroad part-time, given they meet the required demands, such as the physical presence or bona fide residence examinations outlined by the internal revenue service.
Does FEIE Impact My State Tax Obligation Commitments?
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) does not straight impact state tax obligation commitments. useful link States have varying regulations relating to revenue gained abroad, so people should consult their particular state tax obligation guidelines for exact support.
Exist Any Type Of Expiry Dates for FEIE Claims?
Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) insurance claims do not have expiry dates; nonetheless, they must be asserted yearly on income tax return. Failure to case in a given year may result in lost exemption benefits for that year.
How Does FEIE Influence My Social Safety Perks?
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) does not straight influence Social Safety and security advantages, as these advantages are based upon life time earnings. Omitted earnings may reduce general revenues, potentially affecting future benefit estimations.
Can I Revoke My FEIE Insurance Claim After Submitting?
Yes, a person can revoke their International Earned Income Exemption case after filing. This abrogation must be sent with the appropriate tax forms, and it will influence their tax obligation responsibilities and prospective deductions moving forward.
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) provides an essential possibility for U.S. people and resident aliens functioning abroad to minimize their taxable revenue. Recognizing the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE)
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion EarningsFEIE) serves as an essential tax important tax obligation U.S. citizens united state people aliens who work abroad, allowing them permitting exclude an omit portion of part foreign-earned income from Revenue federal united stateGovernment While both the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) and the common deduction serve to reduce taxable income, their interaction can substantially impact a taxpayer's general tax liability. Utilizing the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) can supply significant tax obligation benefits for United state residents and resident aliens living and functioning abroad. Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) insurance claims do not have expiry days; nonetheless, they should be asserted annually on tax returns.